Accounting And Bookkeeping Best Practices for Businesses in the GCC Region
Running a business in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region requires careful attention to accounting and bookkeeping practices. Proper financial management isn't just about keeping your business profitable. Let's learn more.

Team Timber
•
Thu 08 May, 2025

Running a business in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region requires careful attention to accounting and bookkeeping practices. Proper financial management isn't just about keeping your business profitable—it's essential for compliance with regional regulations and for making informed business decisions.
In the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and other GCC countries, specific financial practices are required to maintain legal compliance and optimize operations.
The business landscape in the GCC has evolved significantly over the past decade. With the introduction of Value Added Tax (VAT), corporate tax systems, and stricter regulatory frameworks, businesses need to maintain accurate financial records more than ever. Failing to do so not only risks regulatory penalties but can also prevent you from understanding your business's true financial position.
Regulatory Framework in the GCC
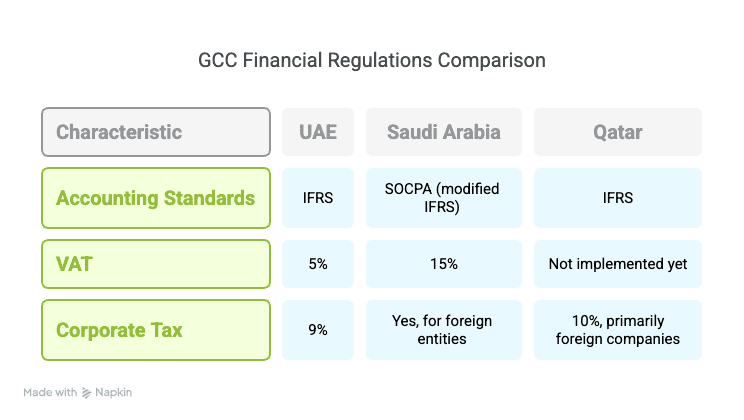
The GCC region operates under a complex regulatory framework that businesses must navigate carefully. Most countries in the region have adopted International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), though often with country-specific modifications. This standardization helps create consistency in financial reporting across borders, but businesses must still be aware of local variations.
In the UAE, IFRS standards form the backbone of financial reporting requirements. The country implemented a 5% VAT system in 2018, which fundamentally changed how businesses track and report financial transactions. More recently, the introduction of corporate tax at 9% has added another layer of compliance requirements for businesses operating in the Emirates.
Saudi Arabia operates under the guidance of the Saudi Organization for Certified Public Accountants (SOCPA), which has adopted IFRS with certain modifications to align with local business practices and Islamic finance principles. The Kingdom has implemented a 15% VAT rate, significantly higher than the UAE, and maintains corporate taxation for foreign entities operating in the country.
Qatar also follows IFRS standards and has implemented a 10% corporate income tax that primarily affects foreign companies. While Qatar has not yet implemented VAT, businesses operating there should prepare for its eventual introduction by establishing robust accounting systems now.
The implementation of VAT across much of the GCC represents one of the most significant shifts in the region's tax landscape. Businesses must register for VAT if they meet the threshold (typically AED 375,000 annual turnover in the UAE), maintain detailed transaction records, issue compliant tax invoices, file regular VAT returns, and preserve financial records for at least five years. This transformation has driven many businesses to upgrade their accounting processes and systems to ensure compliance.
Fundamental Bookkeeping Practices
The foundation of sound financial management in the GCC begins with implementing fundamental bookkeeping practices tailored to the region's requirements.
A well-structured chart of accounts serves as the framework for your entire accounting system. For GCC businesses, this should align with IFRS classification requirements while incorporating region-specific elements such as VAT accounts, withholding tax provisions, and Zakat calculations where applicable. The chart should enable easy extraction of data for compliance reporting and support multi-currency transactions, which are common in the internationally oriented GCC economies.
Daily transaction recording is essential to maintain accuracy and compliance. Businesses should establish processes to record transactions daily, avoiding backlogs that can lead to errors and compliance issues. This includes using consistent classification methods across all entities, implementing proper approval systems for expenditures, strictly separating personal and business expenses (particularly important for family businesses common in the region), and maintaining supporting documentation that meets local requirements.
Bank reconciliation should be performed monthly at minimum. This process identifies discrepancies between your accounting records and bank statements, helps detect potential fraud or errors, ensures all transactions are properly recorded, and maintains accurate cash position reporting. In the GCC, where cash transactions remain common in many sectors, regular reconciliation is particularly important for maintaining financial accuracy.
Petty cash management requires establishing clear policies for usage, implementing a voucher system for disbursements, conducting regular reconciliations, and setting appropriate limits for transactions. In markets like Dubai or Doha where both modern and traditional business practices coexist, proper petty cash management bridges the gap between digital and cash economies.
Documentation management is perhaps the most critical element for GCC compliance. Businesses must store invoices, receipts, and contracts systematically, ensuring documents meet VAT requirements including correct tax registration numbers, accurate VAT calculations, and proper formatting. Both digital and physical copies should be maintained where required by law, and document retention systems should preserve records for at least five years to comply with GCC regulations.
Financial Reporting Requirements
Financial reporting in the GCC requires businesses to prepare several mandatory statements in accordance with IFRS standards. These typically include the Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet), Statement of Profit or Loss (Income Statement), Statement of Cash Flows, Statement of Changes in Equity, and comprehensive Notes to the financial statements that provide additional context and disclosures.
Filing deadlines vary by country but generally include monthly or quarterly VAT returns, annual financial statements, corporate tax returns where applicable, economic substance reporting for certain entities, and Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) disclosures. Missing these deadlines can result in significant penalties, so businesses should maintain a compliance calendar with all relevant due dates.
An important distinction exists between management reporting and statutory reporting. While statutory reports must strictly comply with regulatory requirements and follow prescribed formats, management reports should provide actionable business insights tailored to operational needs. Maintaining both systems and ensuring they can be reconciled is a best practice for GCC businesses, allowing both compliance and informed decision-making.
For business groups operating multiple entities across the GCC, consolidated reporting presents additional challenges. These organizations must consolidate financial statements according to IFRS 10, eliminate intercompany transactions to avoid double-counting, apply consistent accounting policies across all entities despite country-specific variations, and carefully consider tax implications of cross-border operations within and beyond the GCC.
Tax Compliance in the GCC
While the GCC was historically known as a low-tax region, recent years have seen significant changes to the tax landscape, requiring businesses to implement comprehensive tax compliance measures.
VAT recordkeeping forms the cornerstone of tax compliance in countries that have implemented the tax. Businesses should use accounting software that supports proper VAT calculations, correctly classify supplies as standard-rated, zero-rated, or exempt, maintain sequential tax invoice numbering, reconcile VAT reports with accounting records before submission, and carefully track reverse charge mechanism transactions for imported services.
With corporate tax implementation in the UAE and existing systems in other GCC countries, businesses must maintain detailed records of revenue and expenses, track capital expenditures with proper depreciation schedules, document transfer pricing policies for related-party transactions, and prepare for advance tax payments where required. The introduction of corporate tax in the UAE marks a significant shift in the region's approach to taxation, requiring businesses to adopt more sophisticated tax planning strategies.
Withholding tax applies in several GCC jurisdictions, particularly on payments to foreign entities. Businesses must identify transactions subject to withholding tax, calculate and withhold the correct amount, remit it to tax authorities on time, obtain necessary certificates, and maintain detailed records of all withholding tax transactions. This is especially important for businesses with international suppliers or service providers.
Economic substance requirements have been implemented across the GCC to combat tax avoidance. To meet these requirements, businesses must document that they have adequate staff, facilities, and expenditure in the jurisdiction, maintain records of core income-generating activities performed locally, and demonstrate that strategic decision-making occurs within the jurisdiction. Failing to meet economic substance requirements can result in penalties and increased scrutiny from tax authorities.
Technology and Accounting Systems
The right technology infrastructure is essential for effective accounting and compliance in the GCC business environment.
When selecting ERP and accounting software for GCC operations, businesses should ensure the system complies with local VAT and tax requirements, supports Arabic language functionality (often a legal requirement for certain documents), handles multi-currency transactions seamlessly, generates tax-compliant invoices, and produces the specific regulatory reports required in each jurisdiction. Popular solutions include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, Zoho, and QuickBooks, though each should be evaluated against specific GCC requirements.
Cloud-based accounting solutions offer particular advantages for GCC businesses, including real-time financial visibility across multiple locations, automatic backup and enhanced security, easier collaboration with external advisors, and reduced IT infrastructure costs. With improved internet infrastructure across the GCC, cloud solutions have become increasingly viable even for businesses in more remote areas.
Digital transformation of finance functions goes beyond basic accounting software. Forward-thinking GCC businesses are implementing automated data entry solutions to reduce manual processing, electronic invoice processing systems that comply with e-invoicing regulations (already mandatory in Saudi Arabia and expected in other GCC countries), digital approval workflows to streamline operations, integrated banking feeds for real-time cash management, and mobile apps for expense management that are particularly useful for businesses with field staff.
In the UAE specifically, businesses should consider using Federal Tax Authority (FTA) approved software that guarantees compliance with local regulations. These systems generate properly formatted tax invoices, calculate VAT correctly according to UAE rules, create the required VAT return formats, and maintain adequate audit trails to support tax audits. While not always mandatory, using approved software reduces compliance risks.
Internal Controls and Risk Management
Strong internal controls are essential for GCC businesses operating in an increasingly regulated environment.
Effective financial controls ensure transactions are accurately recorded, protect assets from unauthorized use or theft, promote operational efficiency by standardizing processes, and ensure compliance with the growing number of regulations across the region. Basic controls should include approval hierarchies, reconciliation procedures, physical safeguards, and documentation requirements.
Fraud prevention measures are particularly important in environments where cash transactions remain common. Businesses should implement dual approval for payments above certain thresholds, conduct surprise audits of cash-handling functions, rotate responsibilities periodically to prevent opportunity for ongoing fraud, create whistleblower systems to report suspicious activities, and perform background checks on financial staff, particularly those handling cash or with payment approval authority.
Segregation of duties is a fundamental principle of internal control that prevents any single person from controlling multiple parts of a transaction. Businesses should separate transaction authorization from processing, divide recording functions from asset custody, and distribute reconciliation duties across different staff members. In smaller organizations where complete segregation may be challenging, compensating controls such as owner review or external accountant oversight can help mitigate risks.
Clear authorization hierarchies establish transaction amount thresholds for different approval levels, document approval workflows for various transaction types, implement system controls that enforce approval requirements before processing, and maintain logs of all approvals for audit purposes. These hierarchies should reflect both operational needs and risk management principles, with higher-risk or higher-value transactions requiring more senior approval.
Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management is critical in the GCC, where payment terms can be extended and access to financing may be more restrictive than in other markets.
Forecasting techniques should be adapted to the GCC business environment, where seasonality (including effects of Ramadan and summer high temperatures) can significantly impact operations. Businesses should create rolling 13-week cash flow forecasts, update projections weekly based on actual results, include both operating and investing cash flows, and carefully consider regional seasonal fluctuations in their planning.
Working capital optimization helps improve liquidity by implementing efficient inventory management practices, establishing clear credit policies appropriate to the market, setting up structured collections processes with regular follow-up, negotiating favorable payment terms with suppliers, and monitoring key working capital metrics including Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO), Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), and Days Payable Outstanding (DPO).
Managing payment delays requires particular attention in the GCC, where extended payment terms are common in certain sectors. Businesses should include clear payment terms in all contracts, implement systematic follow-up procedures for overdue amounts, consider offering early payment discounts to incentivize prompt payment, use electronic payment methods where possible to reduce processing delays, and monitor aging reports weekly to identify potential issues early.
Building strong banking relationships is essential for managing cash flow effectively. This includes maintaining regular communication with relationship managers, providing timely and accurate financial information to support credit applications, understanding available financing products in the local market, negotiating competitive terms for loans and facilities, and setting up efficient cash pooling structures for groups operating multiple entities across the region.
Outsourcing vs. In-house Accounting
GCC businesses have several options for structuring their accounting functions, each with distinct advantages and considerations.
Outsourcing accounting services in Dubai and other GCC locations can provide access to specialized expertise in regional regulations without maintaining a large internal team, reduce fixed costs associated with employing full-time staff, offer scalability as your business grows, implement best practices developed across multiple clients, and allow management to focus on core business activities rather than administrative functions.
Building an in-house finance team gives businesses more direct control but requires careful planning. Companies taking this approach should hire staff with specific GCC experience and understanding of local regulations, invest in continuous professional development to keep skills current with changing rules, create clear policies and procedures documented in a finance manual, implement robust accounting systems appropriate to local requirements, and establish performance metrics to evaluate the function's effectiveness.
Many GCC businesses benefit from hybrid approaches that combine the advantages of both models. Common arrangements include outsourcing technical functions like VAT compliance that require specialized knowledge, keeping strategic financial planning in-house for better business integration, using external support for monthly close processes to ensure proper oversight, retaining internal control of cash management for security, and outsourcing payroll processing to specialists familiar with the complex requirements of employing a multinational workforce common in the GCC.
Preparing for Audits
Audit requirements in the GCC are becoming increasingly stringent, making preparation essential for smooth compliance.
When selecting auditors, businesses should verify they are registered with relevant local authorities (such as the UAE Accountants and Auditors Association), check their experience in your specific industry sector, assess their understanding of GCC-specific requirements that may differ from global standards, consider their reputation with regulatory authorities in the region, and review their approach to the audit process to ensure it aligns with your business needs.
Pre-audit preparation significantly reduces stress and potential findings. Before auditors arrive, businesses should reconcile all balance sheet accounts to supporting documentation, prepare schedules for major accounts including fixed assets and provisions, organize supporting documentation in a logical and accessible manner, address any outstanding issues from previous audits, and brief your team on the audit process and their responsibilities during the review.
Common audit findings in GCC businesses include inadequate supporting documentation for transactions (particularly for related party dealings), VAT compliance errors such as incorrect tax categorization, revenue recognition issues especially for long-term contracts, insufficient documentation for related party transactions which receive heightened scrutiny, and incorrect provisions and accruals calculations. Being aware of these common issues allows businesses to address them proactively.
After receiving audit findings, implement a structured post-audit action plan by developing a comprehensive response to each finding, assigning specific responsibilities for implementing changes, creating a timeline for addressing findings with priorities for significant issues, documenting process improvements to prevent recurrence, and communicating changes to relevant staff members to ensure consistent implementation.
Wrapping Up!
Implementing robust accounting and bookkeeping practices is not merely a compliance requirement for GCC businesses—it's a strategic advantage in an increasingly regulated and competitive market. With proper financial management, your business can make better-informed strategic decisions based on accurate data, avoid costly penalties and regulatory issues that can damage both finances and reputation, improve cash flow and working capital efficiency, build credibility with banks, investors, and partners, and prepare for growth and expansion with scalable financial systems.
The evolving regulatory landscape in the GCC requires businesses to stay informed and adaptable. Whether you're operating in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, or other Gulf states, investing in proper accounting systems and processes is essential for long-term success and sustainability in a region undergoing significant economic transformation.
How Timber Can Help
Timber Accounting Services combines AI-powered financial technology with expert human oversight to provide comprehensive accounting solutions tailored specifically to GCC businesses.
Our platform automates manual bookkeeping tasks while ensuring compliance with regional regulations through real-time financial dashboards providing instant visibility into your business performance, automated VAT calculations and reporting that comply with local requirements, expert accountants familiar with GCC regulations and best practices, multi-currency support and Arabic language capabilities essential for local compliance, and scalable solutions that grow with your business from startup to enterprise.
Whether you need full outsourced accounting services in Dubai or support for your in-house team, Timber provides the technology and expertise to optimize your financial operations in the GCC region. Our combination of innovative technology and human expertise ensures you receive both efficiency and accuracy in your financial management, allowing you to focus on growing your business while we handle the complexities of GCC accounting compliance.
Simplifying accounting and tax filing for businesses
An AI-powered finance solution, supported by real accountants, to simplify your finances without the high costs or complexity of traditional accounting services.