The A-Z of Back Office Operations for SMBs in UAE and GCC
This guide will walk you through the essential components of back office operations specific to the UAE and GCC markets.

Team Timber
•
Mon 12 May, 2025

Back office operations encompass all the administrative, support, and non-client-facing functions that power a business behind the scenes. For small and medium businesses (SMBs) in the UAE and wider GCC region, these operations form the backbone of organizational efficiency and compliance. While front office activities drive revenue and customer relationships, it's the back office that ensures the business remains compliant, financially sound, and operationally efficient.

SMBs in the UAE and GCC face unique challenges when managing back office operations. The region's complex regulatory environment - characterized by frequent updates to commercial laws, tax regulations, and employment policies—creates a compliance burden that can overwhelm businesses with limited resources. Additionally, the multicultural nature of the workforce, with employees from diverse nationalities and backgrounds, adds complexity to human resource management.
Recent economic diversification efforts across the GCC have introduced new regulations and compliance requirements, further complicating the operational landscape. The introduction of Value Added Tax (VAT), economic substance regulations, Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) documentation, and impending corporate tax in the UAE represent just a few of the recent changes businesses must navigate.
This guide will walk you through the essential components of back office operations specific to the UAE and GCC markets. We'll explore best practices, compliance requirements, technology enablers, and strategic considerations to help SMBs build resilient, efficient, and compliant back office functions that support sustainable growth.
Legal Framework and Compliance
UAE and GCC Business Regulations Overview
The UAE's business regulatory framework operates on multiple levels, creating a complex compliance environment for SMBs to navigate. At the federal level, the UAE Commercial Companies Law (Federal Law No. 2 of 2015, as amended) establishes the foundation for business structures and governance. This law covers company formation requirements, shareholder rights, director responsibilities, and dissolution procedures. Mainland companies must comply with both federal laws and regulations specific to their emirate of registration, typically administered through the Department of Economic Development (DED) or equivalent authority.
Free zones present an alternative regulatory framework. Each of the UAE's 40+ free zones operates under its own regulations, though they must still comply with certain federal laws. Free zones like Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) function as separate legal jurisdictions with their own civil and commercial laws based on English common law principles. Others, like Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA), Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC), and Dubai Silicon Oasis (DSO), maintain regulations aligned with UAE federal law but offer specific advantages for certain business activities.
The regulatory landscape extends beyond company law to include:
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Combating Financing of Terrorism (CFT)
regulations requiring businesses in relevant sectors to implement customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting
Data Protection Laws
that vary by jurisdiction (DIFC Law No. 5 of 2020, ADGM Data Protection Regulations 2021, and Federal Decree Law No. 45 of 2021)
Competition Law
(Federal Law No. 4 of 2012) prohibiting anti-competitive agreements and abuse of dominant market position
Consumer Protection Law
(Federal Law No. 15 of 2020) establishing business obligations toward consumers
Intellectual Property Laws
covering trademarks, patents, and copyrights
Across the wider GCC, regulatory frameworks share similarities but contain important distinctions:
Saudi Arabia has undertaken significant regulatory reform through Vision 2030 initiatives. The new Companies Law of 2015 (amended in 2018) modernized corporate structures, introduced new company types, and simplified formation requirements. The Saudi Arabian General Investment Authority (SAGIA) oversees foreign investment regulations, which have been progressively liberalized to allow 100% foreign ownership in many sectors.
Qatar operates under Law No. 11 of 2015 (Commercial Companies Law), recently amended to allow 100% foreign ownership in most sectors. The Qatar Financial Centre (QFC) provides a separate legal and regulatory framework similar to the DIFC.
Bahrain, Kuwait, and Oman each maintain their own commercial laws with varying degrees of openness to foreign investment, though all have moved toward greater liberalization in recent years.
For SMBs operating across multiple GCC jurisdictions, navigating these different regulatory environments requires sophisticated compliance management systems and often specialized legal support. Practical compliance measures include:
Maintaining a regulatory calendar with key renewal dates and filing deadlines
Implementing a document management system for licenses, certificates, and official correspondence
Establishing relationships with legal advisors familiar with specific jurisdictions
Conducting regular compliance audits
Training key personnel on compliance requirements
Recent Regulatory Changes Affecting SMBs
The past five years have witnessed unprecedented regulatory change across the GCC, fundamentally altering the compliance landscape for SMBs. Understanding these developments is essential for effective back office operations.
Economic Substance Regulations (ESR) were introduced in the UAE in 2019 through Cabinet Resolution No. 31 of 2019 (amended by Cabinet Resolution No. 57 of 2020). These regulations require UAE entities conducting "Relevant Activities" to demonstrate adequate economic presence in the country. The regulations apply to both mainland and free zone companies, including those in financial free zones like DIFC and ADGM.
Relevant Activities include:
Banking
Insurance
Investment Fund Management
Lease-Finance
Headquarters
Shipping
Holding Company
Intellectual Property
Distribution and Service Center
Companies conducting these activities must:
Perform "Core Income Generating Activities" (CIGA) in the UAE
Be directed and managed from the UAE (documented board meetings with quorum physically present)
Maintain adequate employees, premises, and expenditure in the UAE
Submit annual ESR notifications and, if applicable, detailed substance reports
Maintain supporting documentation
Penalties for non-compliance range from AED 20,000 to AED 400,000, with potential suspension, revocation, or non-renewal of trade licenses for repeated violations.
Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) Regulations were implemented through Cabinet Resolution No. 58 of 2020, requiring all UAE entities (excluding those in DIFC and ADGM, which have their own UBO regulations) to identify and report their beneficial owners to the relevant licensing authorities. A beneficial owner is typically defined as an individual who:
Owns or controls 25% or more of the company
Has the ability to appoint or remove the majority of directors
Otherwise exercises significant control over the company or its management
Companies must:
Maintain a register of beneficial owners
Submit UBO information to their licensing authority
Update information within 15 days of any change
Appoint a compliance officer responsible for UBO compliance
Non-compliance can result in fines ranging from AED 100,000 to AED 500,000.
Corporate Tax Introduction represents the most significant recent change to the UAE's financial regulatory landscape. Announced in January 2022 and effective for financial years starting on or after June 1, 2023, the corporate tax regime introduces a 9% tax on business profits above AED 375,000. The framework includes:
0% rate for taxable income up to AED 375,000
9% rate for taxable income above AED 375,000
Different rates for large multinationals and extractive businesses
Exemptions for certain sectors and activities
This fundamental shift requires SMBs to:
Review and potentially restructure operations for tax efficiency
Implement or enhance accounting systems for tax reporting
Develop transfer pricing documentation for related party transactions
Establish tax governance frameworks and controls
Consider implications for shareholder distributions and reinvestment strategies
VAT Updates continue to refine the system introduced in 2018. Recent developments include:
Clarifications on zero-rating and exemptions for specific sectors
Introduction of the "Voluntary Disclosure" system for self-correcting errors
Enhanced rules for input tax recovery
Expanded documentation requirements
Movement toward e-invoicing (expected rollout in coming years)
Labor Law Reforms through Federal Decree-Law No. 33 of 2021 (effective February 2022) overhauled the UAE's employment framework with significant operational implications:
Replacement of unlimited contracts with limited-term contracts (maximum 3 years, renewable)
New work models including part-time, temporary, and flexible arrangements
Enhanced anti-discrimination provisions
Modified end-of-service calculation methods
Revised leave entitlements including study leave and compassionate leave
New termination procedures with minimum notice periods based on service length
For back office operations, these regulatory changes necessitate:
Regular compliance reviews and gap assessments
Enhanced documentation management systems
Updated policies and procedures
Staff training on new requirements
Potential technology investments to support compliance reporting
Financial Management and Accounting
Accounting Standards and Practices
The accounting landscape in the UAE and GCC has evolved toward international standardization, though with important regional variations. The predominant framework is International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), though its application varies by jurisdiction and entity type.
In the UAE, publicly listed companies must follow full IFRS as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). DIFC and ADGM companies are similarly required to prepare financial statements in accordance with IFRS. For other entities, including most SMBs, IFRS adoption is increasingly common but not universally mandated at the federal level. Some companies, particularly smaller entities, may use IFRS for SMEs, which provides simplified reporting requirements while maintaining consistent accounting principles.
For effective financial management, SMBs should establish a comprehensive accounting framework including:
Chart of Accounts Structure: A well-designed chart of accounts should support both operational management and statutory reporting requirements. For UAE businesses, the structure should accommodate:
VAT tracking (separate accounts for standard-rated, zero-rated, and exempt supplies)
Multi-currency transactions with unrealized and realized exchange differences
Department or cost center tracking for management analysis
Project accounting for service businesses
Inventory categorization for trading companies
Fixed asset classifications aligned with tax depreciation categories
Accounting Policies: Formal, documented accounting policies ensure consistency and compliance. Critical policies for UAE/GCC operations include:
Revenue recognition criteria, particularly for long-term contracts
Inventory valuation methods (FIFO, weighted average, etc.)
Fixed asset capitalization thresholds and depreciation methods
Provisions and accruals methodology
Related party transaction identification and documentation
Foreign currency translation approaches
Leases classification and accounting
Month-End Close Process: A structured monthly close enhances financial control and timely reporting. Effective close processes include:
Standardized close calendar with task assignments and deadlines
Revenue and expense accruals
Reconciliation of all balance sheet accounts to supporting documentation
Inventory count procedures (periodic or perpetual)
Fixed asset register updates
Intercompany transaction reconciliations
Management report generation and review
Variance analysis against budget and prior periods
Internal Controls: Financial management requires robust controls to ensure accuracy and prevent fraud:
Segregation of duties, particularly for payment processing and reconciliations
Approval hierarchies with documented authority limits
Regular review of journal entries and supporting documentation
Bank reconciliation by personnel independent from payment processing
Regular reviews of user access rights to financial systems
Surprise cash counts and inventory checks
Vendor master data management with verification procedures
Tax Compliance
The tax environment in the UAE and GCC has transformed dramatically in recent years, creating significant compliance requirements for back office operations.
VAT Compliance is mandatory for businesses exceeding the registration threshold. Detailed requirements include:
Registration Requirements:
Mandatory registration for businesses with taxable supplies exceeding AED 375,000 annually
Voluntary registration option for businesses with supplies exceeding AED 187,500
Group registration possibilities for related entities
Non-resident registration requirements for certain cross-border services
Invoicing Requirements:
Tax invoices must include specific elements:
Supplier name, address, and Tax Registration Number (TRN)
Customer name, address, and TRN (if registered)
Sequential invoice number
Issue date
Supply date or due date for continuous supplies
Description of goods or services
Quantity and unit price
Taxable amount per rate
Tax rate and amount
Total amount payable
Simplified tax invoices permitted for retail transactions under AED 10,000
Arabic language requirements for certain government entities
Filing and Payment:
Quarterly filing for most businesses (monthly for larger entities)
Filing deadline of 28th day following the end of the tax period
Payment due same day as filing
Online submission through Federal Tax Authority (FTA) portal
Detailed tax return with input and output tax breakdown
Supporting schedules for certain transaction types
Record Keeping:
Five-year retention period (extended to 15 years for real estate)
Records must be maintained in original form (physical or electronic)
Arabic translations required if requested by FTA
Records must be kept within the UAE (with some exceptions for cloud storage)
Common Compliance Challenges:
Proper tax treatment of cross-border transactions
Reverse charge mechanism application
Partial input tax recovery calculations
Documentation requirements for zero-rated and exempt supplies
Treatment of deemed supplies and gifts
Bad debt relief procedures
Corporate Tax Preparation has become an urgent priority for UAE businesses. Key implementation considerations include:
System Readiness:
Accounting software configuration for tax calculations
Chart of accounts alignment with tax reporting categories
Fixed asset register setup for tax depreciation
Transfer pricing documentation capabilities
Tax provision calculation methodologies
Structural Considerations:
Legal entity structure review and potential reorganization
Review of intercompany transactions and pricing
Assessment of permanent establishment risks
Evaluation of available exemptions and incentives
Consideration of free zone tax benefits
Compliance Framework:
Tax governance policy development
Tax risk assessment procedures
Documentation requirements definition
Compliance calendar establishment
Resources allocation (internal vs. external expertise)
Financial Reporting Requirements
UAE and GCC businesses must prepare various financial reports to meet statutory requirements and support management decision-making.
Statutory Financial Statements typically include:
Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position):
Assets categorized as current and non-current
Liabilities categorized as current and non-current
Equity components including share capital, reserves, and retained earnings
Comparative figures for the previous year
Income Statement (Statement of Profit or Loss and Other Comprehensive Income):
Revenue breakdown by major category
Cost of sales with appropriate classification
Operating expenses by nature or function
Finance costs separately disclosed
Tax expenses where applicable
Comprehensive income components
Cash Flow Statement:
Operating activities section (typically using indirect method)
Investing activities section
Financing activities section
Reconciliation to cash and cash equivalents
Statement of Changes in Equity:
Movement in share capital
Movement in reserves
Dividend distributions
Total comprehensive income allocation
Notes to the Financial Statements:
Accounting policies summary
Critical accounting judgments and estimates
Detailed breakdowns of major balance sheet items
Related party disclosures
Financial risk management information
Subsequent events disclosure
Going concern assessment
The level of detail required varies by jurisdiction and entity type. DIFC and ADGM entities typically face the most stringent requirements, followed by public joint-stock companies, with private companies having somewhat more flexibility.
Management Reporting supplements statutory reporting with actionable business insights:
Monthly Financial Packages:
Condensed income statement with KPIs
Working capital analysis
Cash flow statement and projections
Segmental analysis by product line, service type, or geography
Headcount and personnel cost analysis
Capital expenditure tracking
Variance Analysis:
Actual vs. budget comparisons
Current period vs. prior period trends
Detailed variance explanations for significant deviations
Corrective action plans for negative variances
Performance Dashboards:
Visual representation of key metrics
Trend analysis with graphical elements
Red/amber/green indicators for KPI status
Drill-down capabilities for deeper analysis
Banking Relationships and Cash Management
Effective banking operations are critical for UAE/GCC businesses given the region's heavy reliance on banking infrastructure for payments and financing.
Banking Setup Considerations:
Account Structure:
Operating accounts in local currency (AED, SAR, QAR, etc.)
Foreign currency accounts for international transactions
Collection accounts for specific revenue streams
Dividend/distribution accounts where relevant
Escrow accounts for regulated activities or specific projects
Electronic Banking:
Dual-control authentication systems
Defined user roles and permissions
Payment approval workflows
Secure access protocols
Mobile banking capabilities
Integration with accounting systems
Trade Finance Facilities:
Letter of credit facilities for imports
Bank guarantee capabilities for tenders and projects
Documentary collection services
Shipping guarantee facilities
Invoice discounting or factoring options
Cash Management Strategies:
Daily Cash Operations:
Beginning-of-day position review
Payment prioritization framework
Intraday liquidity monitoring
End-of-day position reconciliation
Idle fund investment for overnight or short-term periods
Liquidity Optimization:
Cash flow forecasting (13-week rolling basis)
Working capital ratio monitoring
Supplier payment term negotiation
Customer collection strategy implementation
Inventory level optimization
Foreign Exchange Management:
Exposure identification and measurement
Hedging strategy development
Forward contract utilization
Natural hedging through matching currency flows
Regular mark-to-market evaluation
Budgeting and Forecasting
Structured financial planning is essential for navigating the dynamic GCC business environment.
Budget Development Process:
Pre-Budget Preparation:
Macroeconomic research and market analysis
Strategic objective setting and prioritization
Prior year performance review
Key assumption documentation
Budget calendar establishment
Bottom-Up Budgeting:
Departmental template development
Revenue forecasting by product/service line
Headcount planning and personnel cost budgeting
Operating expense detailing by category
Capital expenditure planning with ROI analysis
Budget Consolidation and Review:
Cross-departmental dependency alignment
Consolidated financial statement projection
KPI calculation and evaluation
Multiple scenario testing
Executive review and adjustment
Board approval process
Budget Implementation:
Departmental budget communication
Performance tracking mechanism establishment
Variance reporting framework development
Monthly review cadence implementation
Forecasting Methodologies:
Short-Term Forecasting:
13-week cash flow projections updated weekly
Monthly sales forecasts with pipeline analysis
Inventory requirement projections
Working capital modeling
Medium-Term Reforecasting:
Quarterly budget reforecasting
Year-end projection updates
Scenario analysis based on market developments
Opportunity and risk quantification
Long-Term Financial Planning:
Three to five-year strategic financial plans
Capital structure optimization
Financing requirement identification
Growth initiative financial modeling
Exit or expansion scenario planning
Human Resources Management
Employment Laws in UAE/GCC
The UAE's labor framework is governed primarily by Federal Decree-Law No. 33 of 2021 (effective February 2022), which represents a significant modernization of previous legislation. This law, along with its implementing regulations, establishes comprehensive rules governing employment relationships.
Contract Requirements:
Contract Types:
Limited-term contracts (maximum 3 years, renewable)
No unlimited contracts under new law (existing ones converted)
Part-time contracts (working hours reduced by at least 20%)
Flexible work contracts (varying schedules based on business needs)
Temporary contracts (specific project or time period)
Remote work arrangements
Mandatory Contract Elements:
Employer and employee details
Job title, duties, and work location
Commencement date and duration
Remuneration details including allowances
Working hours and days
Leave entitlements
Notice period and termination conditions
Probation period (maximum 6 months)
Working Conditions Regulations:
Working Hours:
8 hours per day or 48 hours per week standard
Reduction to 6 hours daily during Ramadan for fasting employees
Minimum one-hour daily rest break (not counted in working hours)
Minimum one day off per week
Maximum 2 hours overtime per day with compensation at 125% of normal wage (150% for night work)
Leave Entitlements:
Annual leave: 30 calendar days after one year of service (pro-rated for partial years)
Sick leave: 90 calendar days per year (full pay for first 15 days, half pay for next 30 days, unpaid for remainder)
Maternity leave: 60 calendar days (45 fully paid, 15 at half pay)
Paternity leave: 5 working days
Study leave: 10 working days per year for UAE national employees
Compassionate leave: 5 days for spouse's death, 3 days for parent, child, sibling death
Hajj leave: 30 calendar days once during employment (for Muslim employees)
Termination Provisions:
Notice Requirements:
Minimum 30 days up to maximum 90 days as specified in contract
Payment in lieu of notice option
Employee relieved for reasonable job search time during notice period
Termination Reasons:
Agreement between parties
Contract expiration (if not renewed)
Employer or employee unilateral termination with notice
Termination for cause (specific violations listed in law)
End of Service Benefits:
21 days basic salary per year for first 5 years of service
30 days basic salary per year beyond 5 years
Maximum cap of 2 years' total salary
Calculated on basic salary (excluding allowances)
Pro-rated for partial years
Potential reductions for resignation (dependent on service length)
Other GCC countries have similar but distinct labor regulations:
Saudi Arabia operates under Labor Law Royal Decree No. M/51, with recent reforms expanding employee rights, enhancing job mobility through the removal of previous employer consent for transfers, and introducing more flexible work arrangements.
Qatar's Law No. 14 of 2004 (as amended) has undergone significant modernization, including the landmark removal of the exit permit requirement for expatriate workers and elimination of the No Objection Certificate (NOC) system that previously restricted job changes.
Bahrain, Kuwait, and Oman each maintain their own labor laws with varying provisions regarding nationalization quotas, termination conditions, and working hours, though all have moved toward greater worker protections in recent years.
Visa and Work Permit Processes
Managing employment visas represents one of the most complex back office functions for UAE businesses, requiring meticulous process management and documentation.
Employment Visa Process Flow:
Initial Approval Phase:
Preparation of labor contract meeting Ministry of Human Resources and Emiratization (MOHRE) standards
Job offer letter issuance
Educational certificate attestation (varies by nationality and profession)
Initial approval application submission to MOHRE or free zone authority
Approval receipt and entry permit processing
Entry and Status Change:
Entry permit issuance (valid for 60 days)
Employee entry to UAE
Emirates ID registration and biometric capture
Medical fitness test at government-approved center
Status change processing (for those entering on visit visas)
Labor contract signing and registration
Residence Visa Issuance:
Work permit/labor card issuance
Passport submission for visa stamping
Emirates ID card collection
Medical insurance policy issuance (mandatory in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and most free zones)
Dependent visa processing (if applicable)
The entire process typically takes 2-4 weeks depending on the jurisdiction, nationality of the employee, and specific circumstances. Required documentation includes:
Passport valid for at least 6 months
Educational certificates attested by UAE embassy in country of issuance
Passport-sized photographs with white background
Job offer letter
Labor contract
Entry permit copy
Medical fitness certificate
Emirates ID application
Dependent Visa Considerations:
Eligibility Criteria:
Minimum salary requirement (typically AED 4,000-10,000 depending on profession)
Appropriate accommodation (evidenced through tenancy contract)
Relationship proof (attested marriage certificate, birth certificates)
Process Steps:
Entry permit application with sponsor's income documentation
Medical testing for dependents
Emirates ID registration
Insurance policy issuance
Residence visa stamping
Visa Compliance Management:
Renewal Requirements:
Initiation 30-60 days before expiration
Updated documentation including labor contract
New medical testing
Insurance policy renewal
Fee payment
Cancellation Procedures:
Final settlement calculation and payment
Labor contract cancellation through MOHRE or free zone
Visa cancellation application
Passport visa page cancellation
Gratuity payment documentation
Option for visa transfer to new employer (subject to conditions)
Absconding Reporting:
Official notification requirement if employee is absent for 7+ consecutive days without approved leave
Documentation of communication attempts
Filing through official channels (MOHRE or free zone)
Potential liability implications if not properly reported
Emiratization/Nationalization Policies
GCC countries have implemented increasingly stringent nationalization programs to boost employment of citizens in the private sector. In the UAE, Emiratization policies have evolved significantly in recent years.
UAE Emiratization Framework:
Quota Systems:
Banking sector: 4% annual increase with penalties for non-compliance
Insurance sector: 5% of total workforce
Private sector companies with 50+ employees: 2% of skilled positions annually, reaching 10% by 2026
Classification Systems:
Tawteen Partners Club categorizes companies based on Emiratization performance
Classifications range from Platinum (highest) to Fourth Category (lowest)
Benefits for higher categories include:
Reduced service fees
Priority in government dealings
Higher visa quotas
Exclusivity for certain government tenders
Financial Incentives and Penalties:
Nafis program offering salary support for UAE nationals in private sector
Financial contributions required from non-compliant companies (AED 6,000 monthly per unfilled position)
Potential suspension of services for persistent non-compliance
Implementation Best Practices:
Strategic Recruitment:
Partnerships with UAE national universities
Participation in dedicated Emiratization career fairs
Development of UAE national-specific employer branding
Internship and cooperative education programs
Retention Programs:
Customized career development plans
Mentorship and coaching initiatives
Competitive compensation benchmarking
Recognition programs aligned with cultural values
Cultural Integration:
Cross-cultural training for management
Work environment accommodations for cultural and religious practices
Family engagement initiatives
National identity celebration events
Similar nationalization programs exist across the GCC:
Saudi Arabia's Nitaqat program classifies companies into color-coded categories (Platinum, Green, Yellow, Red) based on Saudization percentages, with corresponding benefits or restrictions. Recent initiatives include the Saudi Employment Strategy aiming to reduce unemployment to 7% by 2030.
Qatar's Qatar National Vision 2030 includes Qatarization targets, with regulated sectors like energy having specific quotas (typically 20-50% depending on the subsector).
Bahrain, Kuwait, and Oman maintain similar programs with varying implementation mechanisms and sector-specific targets.
Payroll Management and WPS Compliance
The Wage Protection System (WPS) represents one of the most significant compliance requirements for UAE employers, mandating electronic salary payments through approved channels.
WPS Requirements and Implementation:
Registration Process:
WPS agent selection (typically a bank or exchange house)
Agent agreement completion
Establishment card registration
Employee bank account documentation
Salary information file template preparation
Monthly Payment Process:
Payroll calculation with appropriate deductions and allowances
SIF (Salary Information File) preparation in prescribed format
SIF submission to WPS agent at least one day before payment
Fund transfer to agent (covering total salary amount plus fees)
Electronic distribution to employee accounts
Receipt of payment confirmation
Timing Requirements:
Payment within 15 days of due date as specified in contract
Regular payment schedule (monthly or more frequent)
Clear documentation of payment date in employment contracts
Common Compliance Issues:
Incorrect SIF formatting leading to rejection
Insufficient funds for complete payroll processing
Delayed submissions resulting in late payments
Inconsistencies between labor contract amounts and actual payments
Unauthorized deductions
Cash payments outside the WPS
Penalties for Non-Compliance:
Fines starting at AED 5,000 and increasing with repeated violations
Potential work permit restrictions
Legal cases through MOHRE
Company classification downgrades
Similar electronic wage payment systems exist across the GCC:
Saudi Arabia's
Wage Protection System requires electronic salary payments with monitoring by the Ministry of Human Resources
Qatar's
Wage Protection System mandates electronic payments through approved financial institutions
Bahrain, Kuwait, and Oman
have implemented or are implementing comparable systems
Comprehensive Payroll Process Elements:
Pre-Payroll Activities:
Time and attendance data collection and verification
Leave management integration
Overtime calculation and approval
Allowance and deduction processing
New hire and termination prorations
Loan and advance management
Payroll Processing:
Gross-to-net calculations
Tax considerations for applicable nationalities
Social insurance calculations (for GCC nationals)
End-of-service benefit accruals
Payment file generation
WPS file creation and submission
Post-Payroll Activities:
Payment confirmation and reconciliation
Payslip distribution (electronic or physical)
General ledger posting and reconciliation
Statutory reporting
Management reporting on personnel costs
Record retention (typically 7+ years)
Employee Benefits Administration
Effective benefits administration is crucial for attracting and retaining talent in the competitive UAE/GCC labor market.
Mandatory Benefits Management:
Medical Insurance:
Abu Dhabi: Comprehensive coverage required for all employees and dependents
Dubai: Basic coverage required for all employees (dependent coverage at employer discretion)
Sharjah and Northern Emirates: No mandatory requirement at emirate level
Coverage requirements vary by jurisdiction:
Minimum annual limit (typically AED 150,000-250,000)
Preexisting condition coverage
Maternity benefits
Network adequacy standards
Work Injury Insurance:
Mandatory coverage for workplace accidents and occupational diseases
Benefit calculation based on severity and basic salary
Reporting requirements to MOHRE within specific timeframes
Return-to-work program documentation
End-of-Service Benefits:
Accurate accrual calculations based on current salary levels
Monthly provision entries in accounting system
Funding strategies (internal accruals vs. external plans)
Payment processing upon termination
Tax implications for certain nationalities
Voluntary Benefits Framework:
Supplementary Medical Coverage:
Enhanced limits beyond mandatory minimums
Expanded network options
Additional benefits (dental, vision, wellness programs)
Executive medical plans for senior management
Insurance Programs:
Life insurance (typically 24-48 times monthly salary)
Disability coverage (short-term and long-term)
Personal accident insurance
Critical illness coverage
Housing and Transportation:
Housing allowance or company accommodation
Transportation allowance or company vehicles
Home leave ticket policies
Relocation assistance
Education Support:
Children's education allowances
Employee continuing education reimbursement
Professional certification support
Conference and workshop participation
Wellness Programs:
Fitness membership subsidies
Health screening initiatives
Mental wellbeing support
Work-life balance policies
Administration Mechanisms:
Policy Documentation:
Comprehensive benefits handbook
Clear eligibility criteria
Enrollment procedures and deadlines
Claims submission processes
Dispute resolution mechanisms
Technology Solutions:
Benefits administration modules in HRIS
Online enrollment platforms
Mobile app access for claims and information
Integration with payroll for automatic deductions
Communication Strategies:
Initial benefits orientation during onboarding
Annual enrollment communications
Multi-lingual materials (considering workforce diversity)
Regular benefits utilization reports
Education sessions on optimal benefits usage
Training and Development Systems
Structured employee development is increasingly important for UAE/GCC businesses seeking to build capabilities and retain talent.
Training Infrastructure Components:
Skills Assessment Framework:
Competency mapping by role and level
Technical and soft skills evaluation
Assessment methodologies (360-degree feedback, knowledge tests, performance evaluation)
Gap analysis against required competencies
Individualized development planning
Learning Management System:
Course catalog management
E-learning module delivery
Training registration and approval workflows
Completion tracking and certification
Learning path customization
Content management capabilities
Delivery Methodologies:
Classroom training facilities and infrastructure
Virtual learning platforms
Blended learning approaches
Microlearning modules for just-in-time knowledge
On-the-job coaching structures
External program selection criteria
Mandatory Training Management:
Compliance Training:
Health and safety (appropriate to industry)
Anti-money laundering and financial crimes (for relevant sectors)
Data protection and information security
Anti-harassment and discrimination
Code of conduct and ethics
Certification Tracking:
Professional license monitoring
Industry-specific certification requirements
Renewal notification systems
Documentation management
Regulatory reporting where required
Performance Management Integration:
Goal Setting and KPI Definition:
Alignment with organizational objectives
SMART criteria application
Weighting methodology
Regular progress monitoring
Adjustment procedures for changing priorities
Review Mechanisms:
Structured review cycles (annual, bi-annual, quarterly)
Self-assessment components
Manager evaluation procedures
Calibration processes for consistency
Documentation requirements
Performance improvement plan protocols
Recognition Programs:
Non-monetary recognition frameworks
Monetary reward structures
Peer recognition systems
Performance-based promotion criteria
Service anniversary celebrations
Cultural considerations for recognition approaches
Technology Infrastructure
Essential Technology Systems for SMB Back Offices
The digital backbone of effective back office operations consists of integrated systems that automate processes, enhance control, and provide actionable insights. SMBs in the UAE and GCC should prioritize the following technology components:
Core Financial Systems:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Accounting Software:
Multi-entity capability for group structures
Multi-currency functionality with automated exchange rate updates
VAT-compliant tax engine with UAE/GCC-specific reporting
Fixed asset management with appropriate depreciation methods
Inventory management with FIFO/LIFO/weighted average costing
Bank integration for automated reconciliation
Financial statement generation aligned with IFRS requirements
Drill-down capabilities for transaction analysis
Role-based access controls with appropriate segregation of duties
Audit trail functionality for compliance purposes
Selection considerations include:
Scalability to accommodate business growth
Local support availability in the UAE/GCC
Arabic language support where required
Compliance with FTA requirements for VAT
Cloud vs. on-premises deployment options
Implementation timeline and resource requirements
Total cost of ownership (licensing, implementation, maintenance)
Popular solutions in the region include SAP Business One, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, Oracle NetSuite, Zoho Books, QuickBooks, and Tally, with selection dependent on business size, complexity, and budget.
Banking and Treasury Management:
Electronic banking platforms with payment initiation and approval workflows
Cash forecasting tools with scenario modeling
Bank fee analysis and optimization
Trade finance management functionality
FX exposure monitoring and hedging tools
Liquidity management dashboards
Bank account reconciliation automation
Expense Management:
Mobile receipt capture and submission
Automated expense categorization and policy compliance checking
Approval workflow configuration
Integration with accounting systems for posting
Reimbursement processing automation
Corporate card management
VAT recovery facilitation
Expense analytics and reporting
Human Resources Systems:
Human Resources Information System (HRIS):
Employee master data management
Organization structure and position management
Document management for employee files
Visa and work permit tracking with expiration alerts
Benefits administration and enrollment
Time-off management with balance tracking
Self-service capabilities for employees and managers
Compensation management with salary structure enforcement
Performance management workflow support
Reporting and analytics dashboards
Payroll Processing:
UAE/GCC-specific calculation rules
WPS file generation and submission
End-of-service benefit computation
Multi-currency handling for expatriate packages
Leave accrual and encashment calculations
Allowance and deduction management
Tax handling for applicable nationalities
General ledger integration
Historical data retention
Compliance reporting capabilities
Recruitment and Applicant Tracking:
Job requisition and approval workflows
Career portal integration
Application screening and ranking
Interview scheduling and feedback collection
Assessment administration
Offer management with approval chains
Onboarding process automation
Candidate communication tools
Analytics for recruitment effectiveness
Integration with HRIS for seamless data transfer
Operations Support Systems:
Document Management:
Centralized repository with version control
Role-based access permissions
Retention policy enforcement
Search functionality with metadata filtering
Annotation and collaboration tools
Mobile access capabilities
Audit trail of document activities
Integration with business applications
Electronic signature capability
Compliance with UAE Electronic Transactions Law requirements
Workflow Automation:
Visual process design tools
Form creation and customization
Approval routing with delegation capabilities
Status tracking and reporting
SLA monitoring and escalation
Integration with core business systems
Mobile approval functionality
Audit logs for compliance purposes
Business Intelligence:
Data warehouse or data lake architecture
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) capabilities
Interactive dashboard creation
Ad-hoc reporting tools
KPI monitoring with alert functionality
Data visualization components
Mobile analytics access
Scheduled report distribution
Data security and governance features
Compliance Management:
Regulatory update tracking
Obligation management and deadline monitoring
Document submission scheduling
Risk assessment tools
Audit preparation support
Training management for compliance topics
Incident reporting and investigation
Remediation tracking
Digital Transformation Roadmap
Implementing technology solutions requires a structured approach to ensure successful adoption and return on investment.
Assessment Phase:
Process Mapping and Optimization:
Current state documentation with process flows
Pain point identification and prioritization
Efficiency opportunity assessment
Compliance gap analysis
Benchmark comparison with industry standards
Process redesign before automation (to avoid digitizing inefficient processes)
Stakeholder input gathering
Future state process mapping
Technology Needs Analysis:
Functional requirements documentation
Technical requirements specification
Integration needs assessment
Scalability considerations
Security and compliance requirements
Mobile accessibility needs
Reporting and analytics requirements
User experience priorities
Current System Evaluation:
Existing technology inventory and assessment
Capability gap identification
Integration limitations
Support and maintenance challenges
License and subscription review
Technical debt quantification
User satisfaction measurement
Total cost of ownership calculation
Implementation Strategy:
Approach Selection:
Big bang vs. phased implementation evaluation
Pilot testing strategy development
Parallel running considerations
Risk mitigation planning
Contingency planning for critical processes
Timeline development with key milestones
Resource allocation planning
Change management strategy
Vendor Selection Process:
Requirements prioritization (must-have vs. nice-to-have)
RFP development and distribution
Vendor response evaluation methodology
Demonstration scripts and scenarios
Reference check protocol
Site visit planning
Scoring system development
Contract negotiation strategy
Service level agreement development
Implementation Planning:
Project team formation with clear roles and responsibilities
Detailed project plan with dependencies
Data migration strategy
Testing methodology (unit, integration, user acceptance)
Training plan development
Go-live readiness assessment criteria
Post-implementation support structure
Success metric definition
Continuous Improvement:
Performance Monitoring:
Key performance indicators alignment with business objectives
System utilization tracking
Process efficiency measurement
User adoption metrics
Return on investment calculation
Exception monitoring and root cause analysis
Support ticket trend analysis
System performance monitoring
User Feedback Collection:
Structured feedback surveys
Focus group sessions
User experience testing
Feature request management
Pain point identification
Success story documentation
User community development
Technology Roadmap Maintenance:
Regular technology assessment against business needs
Update and upgrade planning
New functionality evaluation
Integration opportunity identification
Security and compliance review
Performance optimization planning
User experience enhancement identification
Emerging technology evaluation
Outsourcing vs. In-house Operations
Functions Suitable for Outsourcing
Strategic decision-making around which functions to perform in-house versus outsource requires careful evaluation of various factors. For UAE and GCC businesses, certain back office functions lend themselves particularly well to outsourcing.
Accounting and Financial Functions:
Transactional Accounting:
Accounts payable processing
Accounts receivable management
Bank reconciliation
General ledger maintenance
Fixed asset register management
Month-end close support
Financial statement preparation
Specialized Financial Services:
VAT return preparation and filing
Corporate tax compliance (increasingly important with UAE corporate tax)
Payroll processing and WPS submission
Treasury management
Internal audit execution
External audit preparation support
Financial analysis and reporting
Human Resources Functions:
Administrative HR:
Personnel file maintenance
Leave management administration
Benefits administration
Visa and work permit processing
Employee onboarding and offboarding documentation
HRIS data maintenance
Employee helpdesk services
Specialized HR Services:
Recruitment and candidate screening
Compensation benchmarking
Training delivery
Performance management administration
Employee engagement survey administration
HR compliance monitoring
Business Support Functions:
Administrative Services:
Document management and archiving
Translation services
Reception and front desk operations
Mail and courier management
Office supply management
Facilities management
Travel arrangement services
IT Services:
Helpdesk and technical support
Infrastructure management
Network administration
Cybersecurity monitoring
Backup and recovery management
Application support and maintenance
IT compliance monitoring
Government Relations Functions:
PRO Services:
Company license renewals
Employee visa processing
Document attestation and legalization
Government transaction processing
Translation and typing center coordination
Court representative services
Regulatory filing management
Evaluation Criteria for Outsourcing Decisions:
Strategic Importance Assessment:
Core vs. non-core business activities evaluation
Competitive advantage contribution analysis
Intellectual property considerations
Confidentiality and data sensitivity assessment
Strategic control requirements
Long-term capability development needs
Resource Evaluation:
Internal expertise availability and gaps
Recruitment and retention challenges for required skill sets
Training and development investment requirements
Management bandwidth for function oversight
Physical infrastructure and technology requirements
Scalability needs for business growth
Cost Analysis:
Fully-loaded internal cost calculation (including salaries, benefits, training, facilities, technology)
Outsourcing price models evaluation (fixed fee, transaction-based, time and materials)
Hidden cost identification (transition, management oversight, integration)
Variability of demand assessment
Economies of scale opportunities
Tax and accounting implications
Risk Assessment:
Compliance risk evaluation
Operational risk analysis
Dependency risk assessment
Transition risk identification
Quality control challenges
Business continuity concerns
Reputational considerations
Selecting Service Providers
Choosing the right outsourcing partners is critical for success, particularly in the UAE and GCC where regulatory compliance requirements are significant.
Due Diligence Process:
Technical Capability Assessment:
Service methodology evaluation
Technology infrastructure review
Process documentation quality
Quality control mechanisms
Performance management approach
Continuous improvement philosophy
Problem resolution procedures
Service escalation protocols
Industry Experience Verification:
Client portfolio in similar industries
Understanding of sector-specific regulations
Specialized knowledge demonstration
Case study and success story evaluation
Client reference checks with similar businesses
Industry certification and accreditation
Thought leadership evidence in the sector
Team Qualification Review:
Key personnel experience and qualifications
Team stability and turnover rates
Training and development programs
Staff certification levels
Knowledge transfer mechanisms
Backup staffing arrangements
Cultural fit with your organization
Language capabilities (Arabic, English, others as needed)
Operational Resilience Evaluation:
Business continuity planning
Disaster recovery capabilities
Redundancy in critical systems
Backup procedures and testing
Insurance coverage adequacy
Financial stability assessment
Succession planning for key roles
Geographic distribution of operations
Security and Compliance Verification:
Information security certifications (ISO 27001, etc.)
Data protection policies and procedures
Physical security measures
UAE/GCC regulatory compliance history
Industry-specific compliance capabilities
Privacy controls and GDPR compliance where applicable
Audit rights and transparency
Breach notification procedures
Contractual Considerations:
Service Level Agreements:
Clearly defined service scope with deliverables
Measurable performance metrics
Response and resolution time commitments
Quality standards and acceptance criteria
Reporting frequency and content
Review meeting cadence
Continuous improvement expectations
Performance incentives and penalties
Commercial Terms:
Pricing structure clarity (fixed, variable, hybrid)
Cost escalation mechanisms
Currency and exchange rate provisions
Payment terms and conditions
Expense reimbursement policies
Contract duration and renewal terms
Volume flexibility provisions
Early termination options and costs
Governance Framework:
Roles and responsibilities definition
Decision-making authority matrix
Issue escalation procedures
Change management processes
Performance review mechanisms
Innovation and improvement framework
Communication protocols
Dispute resolution procedures
Risk Management Provisions:
Confidentiality and non-disclosure requirements
Intellectual property ownership
Data security and privacy requirements
Liability limitations and indemnification
Insurance requirements
Force majeure provisions
Regulatory compliance responsibilities
Exit and transition provisions
Managing Outsourced Relationships
Effective governance of outsourcing relationships is essential for realizing the expected benefits while managing risks.
Governance Framework:
Strategic Oversight:
Executive sponsorship assignment
Steering committee establishment with clear charter
Strategic alignment review process
Long-term relationship planning
Value realization assessment
Risk monitoring and mitigation
Innovation and improvement direction
Operational Management:
Day-to-day relationship management roles
Operational meeting cadence (daily, weekly, monthly)
Issue tracking and resolution procedures
Performance dashboard development
Escalation protocols for service issues
Change request management process
Continuous improvement mechanism
Performance Evaluation:
KPI monitoring against targets
Service level agreement compliance tracking
Quality review methodology
User satisfaction measurement
Benchmarking against market standards
Performance review meeting structure
Improvement plan development and tracking
Recognition and reward mechanisms
Integration Strategies:
Process Integration:
End-to-end process mapping with handoff points
Clear responsibility matrix (RACI) development
Standard operating procedure documentation
Joint process improvement initiatives
Exception handling procedures
Escalation protocols for process breakdowns
Process audit methodology
Technology Integration:
System integration requirements definition
Data exchange protocols and standards
Security requirements and controls
Access management and authentication
Change management coordination
Testing and validation procedures
Disaster recovery synchronization
Technology roadmap alignment
People Integration:
Cultural alignment initiatives
Joint training programs
Knowledge sharing mechanisms
Relationship building activities
Communication protocol development
Feedback channels establishment
Career development opportunities
Recognition and appreciation programs
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Comprehensive evaluation of outsourcing decisions requires thorough analysis of both quantitative and qualitative factors.
Quantitative Factors:
Direct Cost Comparison:
Internal labor costs (salaries, benefits, bonuses, training)
Facility costs (office space, utilities, equipment, maintenance)
Technology costs (software licenses, hardware, support, upgrades)
Management overhead allocation
Regulatory compliance costs
Quality control expenses
Outsourcing service fees (base fees, transaction fees, one-time costs)
Transition and implementation costs
Contract management costs
Potential penalty or incentive payments
Financial Impact Analysis:
Cash flow implications
Capital expenditure vs. operating expenditure considerations
Tax implications
Balance sheet impact
Working capital effects
Foreign exchange exposure (for offshore outsourcing)
Financial ratio impacts
Cost variability analysis
Scalability cost curves
Risk-Adjusted Return Calculation:
Expected cost savings probability distribution
Service quality risk quantification
Business disruption risk valuation
Compliance failure risk assessment
Transition failure risk evaluation
Vendor financial stability risk analysis
Reputational risk valuation
Exit cost estimation
Qualitative Considerations:
Strategic Alignment:
Core competency focus enhancement
Management attention reallocation to strategic activities
Market responsiveness improvement
Innovation capability impact
Competitive positioning effects
Organizational agility enhancement
Strategic flexibility preservation
Growth enablement potential
Operational Benefits:
Process standardization opportunities
Best practice implementation
Access to specialized expertise
Technology advancement acceleration
Scalability improvement
Business continuity enhancement
Service quality improvement
Performance management discipline
Organizational Impact:
Employee morale and engagement effects
Organizational culture implications
Knowledge retention considerations
Skills development opportunities
Change management requirements
Communication challenges
Management complexity
Organizational structure impacts
Hybrid Operational Models
Many UAE and GCC businesses find that a hybrid approach to back office operations provides the optimal balance between control and efficiency.
Common Hybrid Approaches:
Function Segmentation:
Strategic vs. transactional separation (e.g., financial planning in-house, transactional accounting outsourced)
Specialized vs. routine division (e.g., complex tax planning in-house, VAT return preparation outsourced)
Core vs. supplementary split (e.g., compensation strategy in-house, benefits administration outsourced)
Sensitive vs. standard information handling (e.g., executive payroll in-house, general staff payroll outsourced)
Process Segmentation:
Front-end vs. back-end division (e.g., customer-facing accounts receivable in-house, collections outsourced)
Approval vs. execution separation (e.g., payment approval in-house, payment processing outsourced)
Exception vs. standard handling (e.g., complex transactions in-house, routine transactions outsourced)
Design vs. execution split (e.g., report design in-house, regular report generation outsourced)
Geographic Segmentation:
Headquarters vs. branch operations (e.g., corporate accounting in-house, branch accounting outsourced)
Home market vs. expansion markets (e.g., UAE operations in-house, other GCC operations outsourced)
Strategic market vs. secondary market division (e.g., Saudi operations in-house, other markets outsourced)
Regulated vs. less regulated market separation (e.g., DIFC operations in-house, mainland operations outsourced)
Implementation Considerations:
Governance Structure:
Integrated governance framework spanning in-house and outsourced components
Clear decision rights and accountability definition
Coordinated planning and budgeting processes
Joint performance management system
Aligned incentive structures
Comprehensive risk management approach
Unified compliance monitoring
Integrated escalation protocols
Process Design:
End-to-end process mapping with clear handoff points
Responsibility matrix development with no gaps or overlaps
Exception handling procedures spanning both models
Knowledge sharing mechanisms between internal and external teams
Continuous improvement framework encompassing all parties
Standard terminology and definitions across operations
Joint process review cadence
Technology Integration:
Single source of truth establishment
Data synchronization mechanisms
Integrated workflow management
Consistent technology standards
Coordinated change management
Unified security framework
Compatible disaster recovery approaches
Aligned technology roadmaps
Innovation and Future Trends
Artificial Intelligence in Back Office Operations
AI technologies are transforming back office operations from labor-intensive, error-prone processes to intelligent, automated systems that enhance accuracy while reducing costs.
Current Applications:
Intelligent Document Processing:
Automated data extraction from invoices, receipts, and contracts
Natural language processing for unstructured document analysis
Classification of documents by type, content, and priority
Validation of extracted data against business rules
Exception handling with human-in-the-loop processes
Continuous learning from processing patterns
Integration with workflow systems for straight-through processing
Financial Operations Automation:
Anomaly detection in financial transactions
Automated account reconciliation
Predictive cash flow forecasting
Intelligent payment matching
Fraud pattern detection
Automated financial reporting generation
Audit sample selection optimization
Tax calculation and optimization
Human Resources Enhancement:
Resume screening and candidate matching
Employee query handling through conversational AI
Onboarding process automation
Employee sentiment analysis
Attrition prediction and prevention
Talent analytics for workforce optimization
Learning recommendation engines
Performance pattern analysis
Compliance and Risk Management:
Regulatory change monitoring and impact assessment
Transaction screening against sanctions and PEP lists
Contract analysis for compliance requirements
Automated regulatory reporting
Risk pattern identification
Control effectiveness testing
Audit finding prediction
Compliance training personalization
Implementation Considerations:
Data Readiness Assessment:
Data quality evaluation
Data standardization requirements
Historical data availability for training
Data governance framework
Privacy and security considerations
Data integration capabilities
Ongoing data maintenance plans
Master data management approach
Solution Evaluation:
Make vs. buy decision methodology
Vendor assessment criteria
Pilot project design
Success metric definition
Scalability evaluation
Integration requirements
Total cost of ownership calculation
Return on investment projection
Change Management:
Workforce impact assessment
Skill gap identification
Upskilling and reskilling programs
Communication strategy development
Adoption incentive design
New role definition
Career progression redesign
Cultural change management
Governance and Ethics:
Algorithmic bias prevention
Decision explainability requirements
Human oversight mechanisms
Ethical use framework
Regular algorithm auditing
Continuous monitoring procedures
Stakeholder engagement process
Regulatory compliance verification
Preparing for Technological Disruption
The pace of technological change continues to accelerate, requiring SMBs to develop systematic approaches to evaluating and adopting emerging technologies.
Strategic Approaches:
Technology Radar Development:
Systematic scanning of emerging technologies
Relevance assessment methodology
Impact estimation framework
Implementation difficulty evaluation
Risk assessment process
Investment prioritization criteria
Adoption timeline planning
Regular review cadence
Innovation Culture Building:
Innovation mindset development
Idea generation processes
Cross-functional collaboration mechanisms
Experimentation frameworks
Failure tolerance establishment
Recognition systems for innovation
Resource allocation for exploration
Success story communication
Strategic Partnering:
Technology ecosystem development
Startup engagement programs
Academic institution collaboration
Industry consortium participation
Co-creation initiatives
Innovation hub engagement
Knowledge sharing networks
Joint venture exploration
Capability Development:
Digital literacy programs
Technical skill building
Innovation methodology training
Change management capability enhancement
Agile project management skill development
Data analysis capability building
Design thinking methodology adoption
Technology evaluation skill development
Emerging Technologies to Monitor:
Blockchain Applications:
Smart contracts for automated compliance
Secure document verification and authentication
Supply chain traceability and verification
Immutable audit trails for regulatory compliance
Digital identity management
Secure multiparty transaction processing
Tokenization of assets and liabilities
Cross-border payment optimization
Advanced Analytics:
Predictive analytics for business forecasting
Prescriptive analytics for decision optimization
Natural language generation for automated reporting
Computer vision for document processing
Speech analytics for customer interaction analysis
Graph analytics for relationship mapping
Geospatial analytics for location-based insights
Simulation modeling for scenario planning
Cloud Evolution:
Serverless computing models
Containerization for application portability
Microservices architectures
Edge computing for latency-sensitive applications
Multi-cloud strategies for risk distribution
Cloud-native security approaches
API-based integration frameworks
Consumption-based pricing models
Automation Expansion:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for routine tasks
Low-code/no-code development platforms
Intelligent process automation combining RPA and AI
Cognitive automation for judgment-based tasks
Conversational interfaces for system interaction
Workflow orchestration platforms
Decision automation frameworks
Autonomous agents for complex tasks
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Building effective back office operations for SMBs in the UAE and GCC requires a multifaceted approach that balances regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and strategic alignment. Key success factors include:
Regulatory Vigilance: The rapid pace of regulatory change in the region demands continuous monitoring and systematic implementation processes. From VAT to corporate tax, ESR to UBO regulations, staying ahead of compliance requirements is essential for avoiding penalties and business disruptions.
Financial Discipline: Robust financial management with appropriate controls, standardized processes, and comprehensive reporting forms the foundation of sustainable operations. Adopting appropriate accounting standards, implementing effective cash management practices, and establishing clear financial governance are critical success factors.
Human Capital Optimization: Navigating the complex employment landscape of the GCC requires specialized knowledge and systematic processes. From visa management to WPS compliance, Emiratization to end-of-service benefits, human resources operations demand meticulous attention to detail and proactive management.
Technology Enablement: Leveraging appropriate technology solutions can transform back office operations from cost centers to strategic enablers. Selecting and implementing systems that support compliance, enhance efficiency, and provide actionable insights is increasingly essential for competitive advantage.
Strategic Outsourcing: Thoughtful decisions about which functions to perform in-house versus outsource allow SMBs to access specialized expertise while controlling costs and maintaining appropriate oversight. Hybrid operating models often provide the optimal balance between control and efficiency.
Innovation Mindset: Embracing emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and advanced analytics can drive step-change improvements in back office performance. Developing systematic approaches to evaluating and adopting innovations positions SMBs for long-term success.
Building a Resilient Back Office Operation
Resilience in back office operations—the ability to maintain essential functions despite disruptions—has become increasingly important in the dynamic GCC business environment.
Process Documentation and Standardization: Comprehensive documentation of processes, policies, and procedures ensures consistency and facilitates knowledge transfer. Standard operating procedures should cover normal operations, exception handling, and contingency scenarios.
Cross-Training and Knowledge Management: Reducing key person dependencies through systematic cross-training and knowledge sharing minimizes operational risks. Documentation, job rotation, and collaborative tools help distribute institutional knowledge across the organization.
Technology Redundancy: Implementing appropriate backup systems, disaster recovery capabilities, and business continuity technologies ensures critical functions can continue despite technical disruptions. Cloud-based solutions often provide inherent resilience advantages.
Compliance Monitoring Systems: Proactive compliance management through systematic monitoring, regular self-audits, and robust governance helps identify and address issues before they become significant problems.
Scenario Planning: Developing response plans for various disruption scenarios—from regulatory changes to system failures, staff unavailability to market disruptions—enhances organizational readiness and minimizes reaction time.
Adaptable Structures: Creating flexible organizational designs, scalable technology architectures, and modular process frameworks allows for rapid adaptation to changing business conditions and regulatory requirements.
How Timber Can Help with Back Office Operations
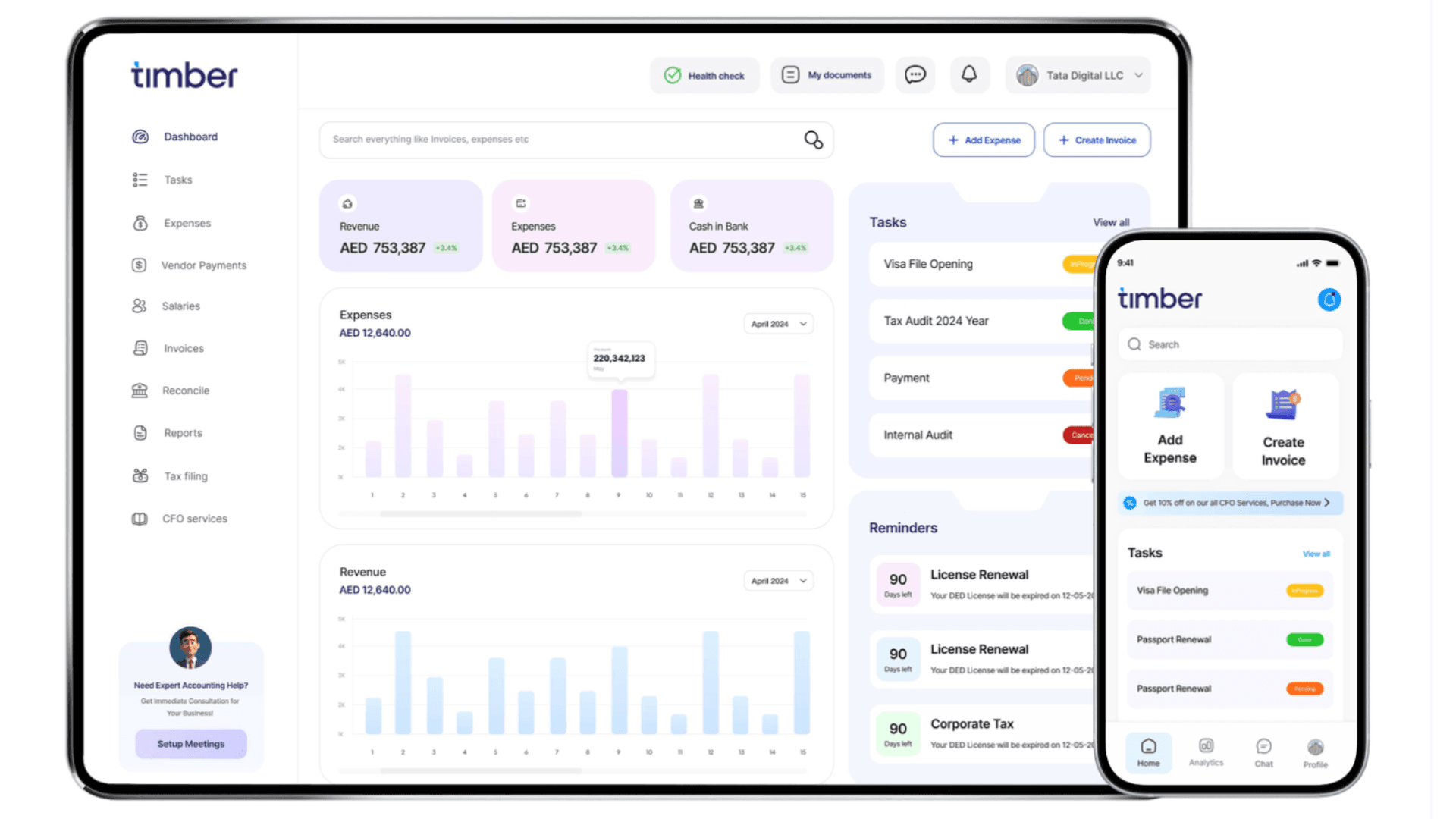
Timber provides comprehensive back office support for SMBs in the UAE and GCC, combining advanced technology with regional expertise to deliver efficient, compliant operations at scale.
AI-Powered Financial Management: Our platform leverages artificial intelligence to automate routine accounting tasks while providing real-time visibility into financial performance. From automated data extraction to intelligent account reconciliation, predictive analytics to anomaly detection, our AI capabilities transform financial operations.
UAE (and other GCC)-Specific Compliance Solutions: Our systems and processes are designed specifically for the UAE and GCC regulatory environment. We maintain continuous monitoring of regulatory changes, implement updates promptly, and ensure your operations remain fully compliant with VAT requirements, ESR regulations, UBO reporting, and the upcoming corporate tax framework.
Integrated Human Resources Management: Our comprehensive HR solutions address the unique challenges of workforce management in the UAE. From visa processing to WPS compliance, Emiratization strategy to end-of-service benefit management, we provide both technology platforms and expert services to optimize your human capital operations.
Flexible Service Models: Recognizing that each business has unique needs, we offer customizable service packages ranging from fully managed outsourcing to targeted support for specific functions. Our hybrid delivery models combine technology platforms, remote services, and on-site support to create the optimal solution for your business.
Technology Advisory and Implementation: Beyond operational services, we provide strategic guidance on technology selection, implementation support, and change management assistance. Our team helps you navigate the complex technology landscape to find solutions that fit your specific requirements and budget.
Scalable Solutions: As your business grows, our services and systems grow with you. From startup to scale-up, our solutions adapt to your changing needs without requiring disruptive transitions or costly system replacements.
With deep regional experience, cutting-edge technology, and a commitment to excellence, Timber helps SMBs build efficient, compliant, and scalable back office operations that support sustainable growth in the dynamic UAE and GCC markets. Contact us today to discover how we can transform your back office into a strategic advantage for your business.
Simplifying accounting and tax filing for businesses
An AI-powered finance solution, supported by real accountants, to simplify your finances without the high costs or complexity of traditional accounting services.